What Is Bloom’s Revised Taxonomy?
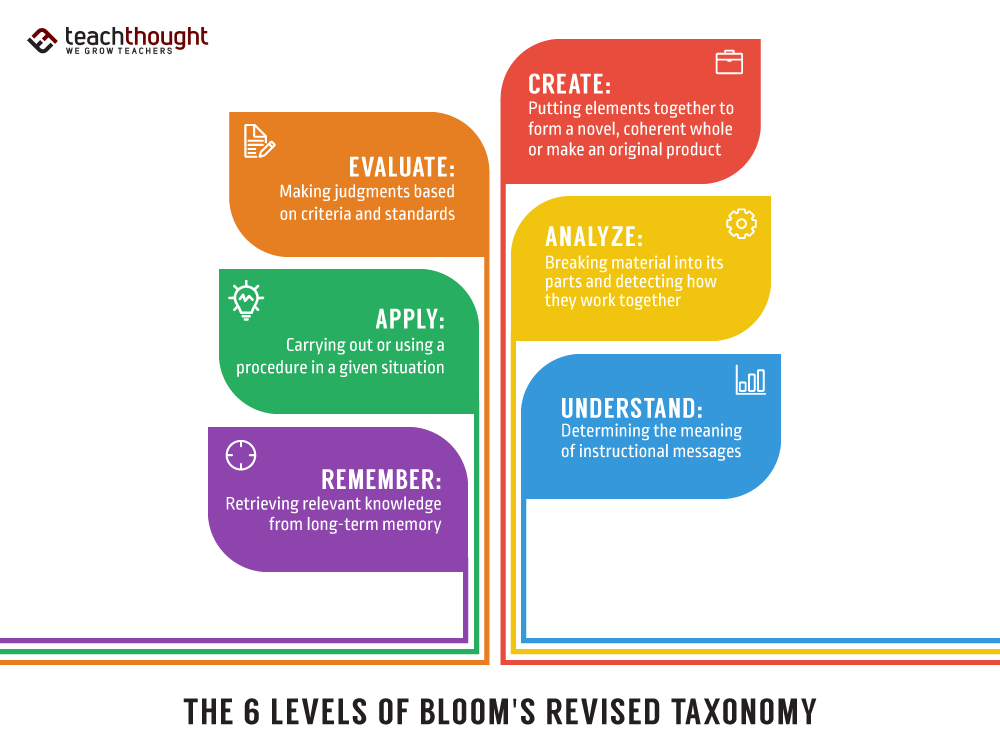

Bloom’s Revised Taxonomy modified the unique 1956 framework by updating the extent names to verbs, reordering the highest ranges, and including a second dimension for kinds of data. The revision clarifies what college students do cognitively and the way these actions work together with factual, conceptual, procedural, and metacognitive data.
How Bloom’s Taxonomy Modified
- Nouns to verbs: ranges reframed as cognitive actions: Bear in mind, Perceive, Apply, Analyze, Consider, Create.
- High-level reorder: Create positioned above Consider to replicate generative considering.
- Two dimensions: pair the Cognitive Course of with the Information Dimension (Factual, Conceptual, Procedural, Metacognitive).
- Clearer alignment: aims, instruction, and evaluation mapped with the Taxonomy Desk.
- Modernized language: Comprehension turns into Perceive; Information turns into Bear in mind.
- Planning influence: encourages job verbs and proof of studying slightly than class labels.
Unique vs Revised Degree Names
| Unique (1956) | Revised (2001) |
|---|---|
| Information | Bear in mind |
| Comprehension | Perceive |
| Software | Apply |
| Evaluation | Analyze |
| Synthesis | Create |
| Analysis | Consider |
What Modified Past the Phrases
The revision launched the Taxonomy Desk: a grid that crosses six cognitive processes with 4 data sorts. This helps lecturers specify outcomes and assessments extra exactly, for instance, Analyze x utilizing conceptual data or Apply y utilizing procedural data.
- Information Dimension: Factual, Conceptual, Procedural, Metacognitive.
- Course of–data pairing: clarifies job design and proof high quality.
- Evaluation implications: verb selection indicators anticipated considering and scoring focus.
Why It Was Revised
From 1995 to 2000, a workforce led by Lorin Anderson and David Krathwohl up to date Bloom’s Taxonomy to replicate modern cognitive science and classroom evaluation observe. The purpose was to honor the unique whereas making it extra actionable for planning, instruction, and analysis.
Reference: David R. Krathwohl (2002). A Revision of Bloom’s Taxonomy: An Overview. Principle Into Follow, 41(4), 212–218.

